An introduction to carbonyl compounds
Aldehydes and ketones:
 |
 |
| Aldehyde | Ketone |
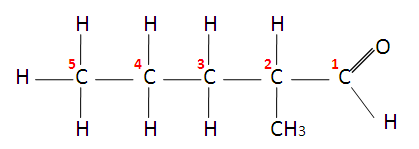
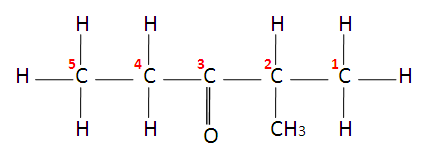
Ketones end in ‘one’ and have a carbonyl group ( C = O ) with 2 alkyl groups attached.
p's to p's
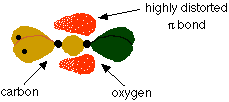
Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen:

The difference in this set up is the difference in electronegativities of the carbon and oxygen atom.
Oxygen is much more electronegative than carbon meaning that the p electrons will be highly distorted towards the oxygen atom as shown above.
 |
This sets up a permanent dipole across the C=O bond:
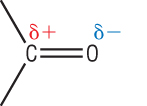
Naming aldehydes and ketones:
Aldehydes and ketones are named in the same way as in AS:
 |
 |
| 2-Methylpentanal | 2-methylpentan-3-one |
In aldehydes, the aldehyde carbon always starts at 1.
In ketones, the ketone (or carbonyl group) is always counted to give it the smallest possible number.
Aromatic aldehydes and ketones:
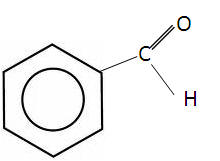
The simplest aldehyde is benzaldehyde and the simplest ketone is phenylethanone:
 |
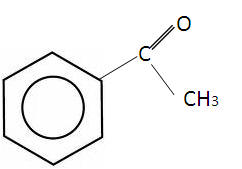 |
| Benzaldehyde | Phenylethanone |
These aromatic aldehydes and ketones have a fragrant smell, often found naturally in foods.
Qu 1 - 4 P21
Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes
In unit 2, module 2 we oxidised primary, secondary alcohols and aldehydes further.
Tertiary alcohols however could not be oxidised further.
We used acidified dichromate, H+ / Cr2O72- to oxidise (usually as sulphuric acid and potassium dichromate).
We noticed that if we oxidise alcohols:
Primary alcohols:
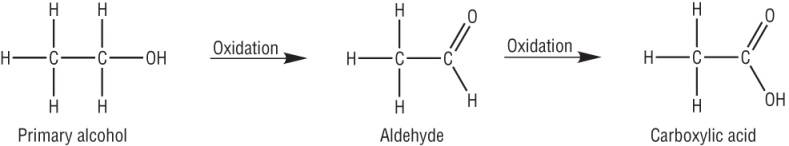
| CH3CH2OH | + | [O] | à | CH3CHO | + | H2O |
| CH3CH2OH | + | 2[O] | à | CH3COOH | + | H2O |
Secondary alcohols:
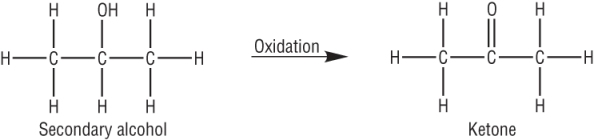
| CH3CHOHCH3 | + | [O] | à | CH3COCH3 | + | H2O |
Aldehydes:
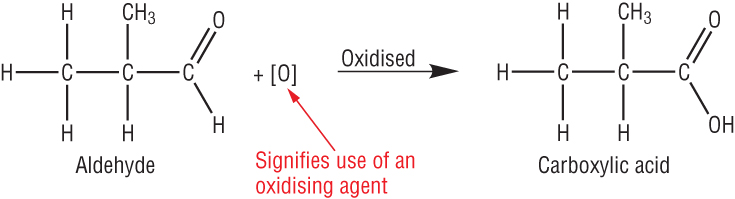
| CH3CHO | + | [O] | à | CH3COOH | + | H2O |
Qu 1 - 3 P23
Reactions of aldehydes and ketones
Reducing aldehydes and ketones
Nucleophilic addition reactions:
|
|
The Mechanism:

Qu 1 - 4 P 25
Chemical tests on carbonyl compounds
|
Reaction |
Aldehyde |
Ketone |
|
2.4-DNPH |
A yellow / orange crystalline solid is formed |
A yellow / orange crystalline solid is formed |
|
Tollen’s reagent |
A silver mirror is formed as Ag+ is reduced to Ag |
No reaction |
|
Oxidation with acidified sodium dichromate (VI) (from AS) |
Orange to green, as Cr6+ is reduced to Cr3+ |
No reaction |
The orange crystals from 2,4-DNPH can be filtered, recrystallised and melting point determination. Once you know whether it is an aldehyde or ketone from Tollen's reagent, look up the MPt of the derivative in a table to identify the crystals and hence the aldehyde / ketone.
Qu 1 - 3 P27
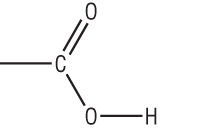
Introduction to carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids have the general formula:
 |
These are present in many foods:
Ethanoic acid – vinegar
Benzoic acid – used as flavouring in lemonade
Citric acid – Used as flavouring in citrus drinks
1) Solubility and pH
Solubility – C1 - C4 carboxylic acids mix readily:
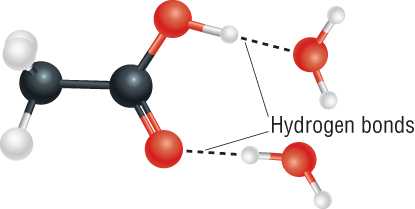
C5 à solubility reduces due to length of insoluble R chain.
All carboxylic acids H - bond to each other and with water.
Acid reactions of carboxylic acids:
Carboxylic acids are weak acids as they partially dissociate in water.
They react as acids to form salts called carboxylates.
Less than 1% ionised:-
RCO2H(aq) à H+(aq) + RCO2-(aq)
2. Formation of salts:
Carboxylic acids are acidic enough to react with:
Metals Metal hydroxides Metal carbonates
They react in the usually acidic way making salts, hydrogen, water or water and carbon dioxide.
 |
|
a) With magnesium
2CH3CO2H + Mg à (CH3CO2)2Mg + H2
Magnesium ethanoate
b) With sodium hydroxide
CH3CO2H + NaOH à CH3CO2Na + H2O
Sodium ethanoate
c) With sodium carbonate
2CH3CO2H + Na2CO3 à 2CH3CO2Na + H2O + CO2
Sodium ethanoate
In each case the carboxylic acid has donated a proton, H+
A salt is formed each time
Qu 1 - 2 P29
Esters have the general formula:
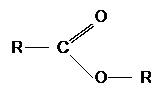
Esters are referred to as a derivative of carboxylic acids due to the easy substitution of the hydrogen in the hydroxyl group with an alkyl group. They are derived from carboxylic acids.
Again these are found in foods and have a fruity aroma.
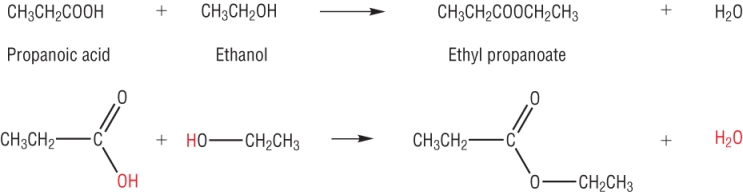
Making esters:
From AS you made esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols using an acid catalyst and heat.
The reaction is known as esterification. It is a reversible reaction (later) and the yield of ester was low:
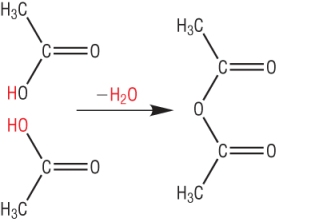
Esters from acid anhydrides
Esters can be produced from acid anhydrides with gentle heating.
This gives a better yield of ester as acid anyhdrides are a lot more reactive than carboxylic acids:
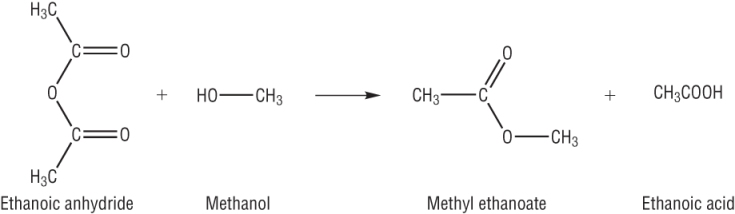
The reaction:
Ester hydrolysis:
This is the break down of esters with the reaction with water.
Ester + water à Carboxylic + Alcohol
acid
It is the reverse reaction of the esterification reaction.
Carboxylic + Alcohol à ester + water
acid
It can be done using an acid or alkaline catalyst. The products formed are slightly different:
1) Acid hydrolysis:
The hydrolysis of any carboxylic acid derivative results in the carboxylic acid.
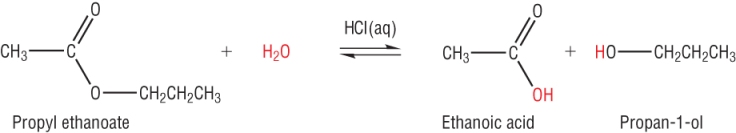
The reaction is in equilibrium which means molecules of reactants and products are present in the reaction mixture.
2) Alkaline hydrolysis:
When a base is used, the product is the sodium salt of the carboxylic acid:
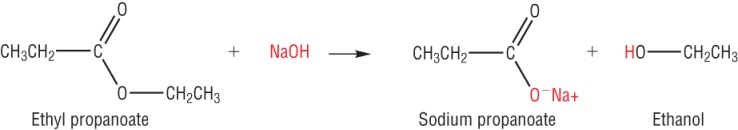
The reaction is non reversible which means that only products are present in the final reaction mixture.
This reaction is also called 'saponification' as soaps are made in this way by the hydrolysis of fats (later).
Esters as perfumes and flavourings:
Esters occur naturally in foods and flowers so can be used as perfumes.
Esters are also found in essential oils, 'oil of wintergreen' used as deep heat.
Benzyl ethanoate gives and apple and pear flavour / smell.
Qu 1 - 3 P31
Fats and oils - building triglycerides
Fats and oils:
Fats and oils are basically esters made from propan-1,2,3-triol or glycerol (a triol) and long chain carboxylic acids, fatty acids:
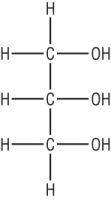 |
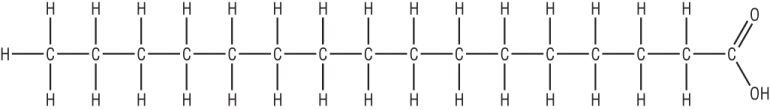 |
| Glycerol | Long chain carboxylic acid, fatty acid - hexadecanoic acid |
Its melting point determines whether it is a fat or oil.
If its melting point is above room temperature it is a solid which makes it a fat, eg margarine and butter.
If its melting point is below room temperature it is a solid which makes it an oil, eg olive oil.
Triglycerides - the building blocks:
Triglycerides are naturally occurring fats. They are triesters of propan - 1,2,3 - triol, glycerol and fatty acids.
Glycerol has 3 alcohol groups which can react with a carboxylic acid (stearic acid) to form an ester.
If all 3 join we make a triglyceride (an ester).
The carboxylic acids occur naturally and because they make fats (upon esterification) we call them fatty acids.
Fatty acids are saturated if they contain only C - C and unsaturated if they contain C=C.
Fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms due to their synthesis in nature.
A saturated fatty acid: Hexadecanoic acid (palmitic acid)

Has no C = C
A monounsaturated fatty acid: Octadec - 9 - enoic acid (oleic acid)
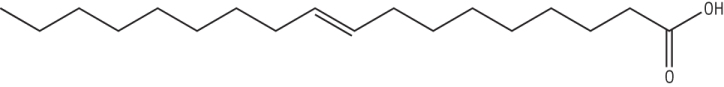
Has 1 C = C between Carbon 9 and 10 (common)
A polyunsaturated fatty acid: Octadec - 9,12 - enoic acid (linoleic acid)
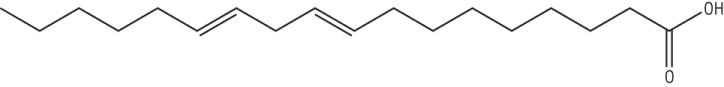
Has 2 C = C between Carbon 9 and 10 / 12 and 13
Fatty acid - shorthand:
Fatty acids can be written in shorthand:
| Number of carbon atoms | Number of double bonds | Position of double bonds | |
| 18 | : | 1 | (9) |
 |
16:0 |
 |
18:1 (9) |
 |
18:2 (9.12) |
Forming triglycerides:
These are basically esters:
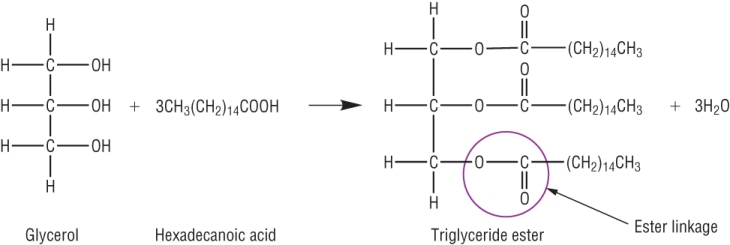
Most triglycerides (fats) actually form using different fatty acids
Triglycerides (fats) can be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the fatty acids they are made of are saturated or not
Qu 1 - 4 P33
Triglycerides, diet and health
Isomerism in unsaturated fatty acids:
In AS we covered the Cis Tranz (E/Z) isomerism involving a C=C:
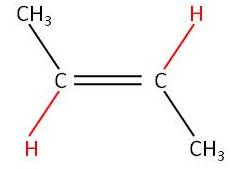 |
No free rotation around the C=C |
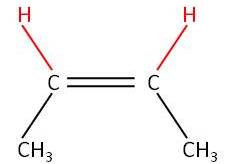 |
| Trans
but-2-ene (E-but-2-ene) |
Cis
but-2-ene (Z-but-2-ene) |
Remember the C=C stops free rotation around the C=C.
Fats and oils come from saturated and unsaturated fatty acids:
| Fatty Acid | Risk | Reason | Packing | State | Cause | |
| Saturated | Heart disease | Raises blood cholesterol | Close | Solid | Blocks arteries | |
| Unsaturated | Trans | Coronary heart disease | Raises blood cholesterol | Close | Solid | Blocks arteries |
| Cis | No Health risk | Cannot pack close together | Liquid | No effect | ||
Unsaturated packing:
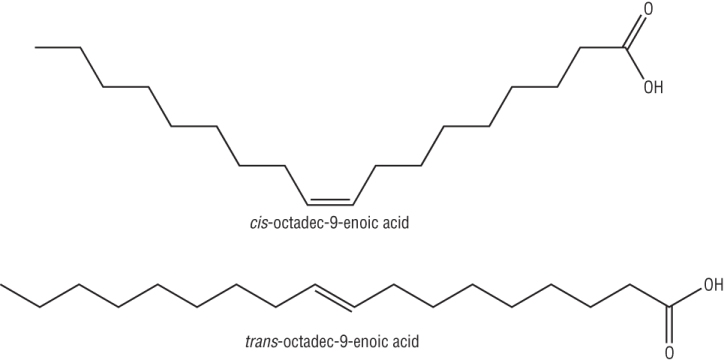 |
Non linear - inefficient packing - liquid |
| Linear - efficient packing - solid |
The food industry often removes some of the C=C by hydrogenation (adding H2 across the C=C)
This makes them more solid = margarine manufacture.
A side effect of this is that the structure of the fat is changed from a liquid (little health risk) to a solid (Heart risk)
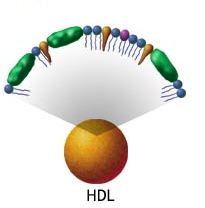
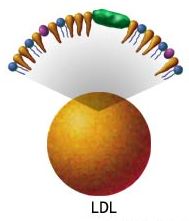
Trans fats cholesterol:
| High Density Lipoproteins | Low Density Lipoproteins |
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
Fatty Acids as Biodiesel:
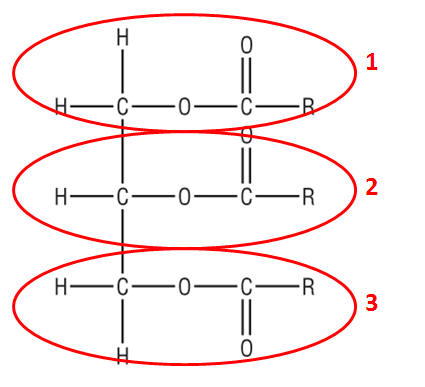 |
TRANSESTERIFICATION
|
Making Biodiesel - Transesterification:
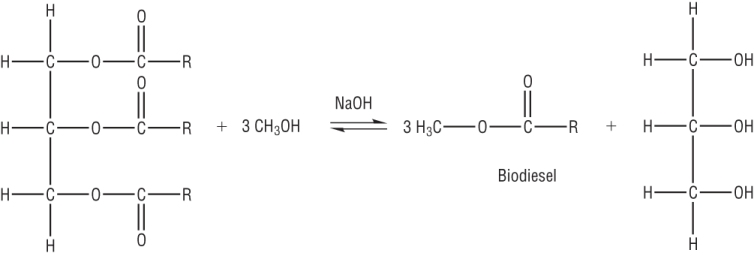
The waste oil is filtered then reacted with methanol and sodium hydroxide (catalyst) to form biodiesel.
This also increases the atom economy of fats.
Qu 1 - 4 P35
Qu 5 - 8 P41 / 4 - 10, 14 P42 - 45